Microsoft Windows is a multi-user operating system. The "Log On" options in AutoMate allow the user to specify under which user context a task should run when it is triggered (started automatically). By default, a task will run under the context of the currently logged in user. This means that if an AutoMate task were to launch an application, the registry, mapped drives external application preferences and other settings will map to the current user. By specifying an alternate user account, AutoMate can optionally map all user specific settings (including external application preferences and layouts) to the alternate user while the task is running.
When a Windows machine is logged off there is no current user, thus an option is also available to control how this condition is handled. The default behavior is to logon as the default user (specified in the AutoMate System Options under Run As) and run the task. The user may also specify not to run the task at all, or to run as a specific alternate user.
The Windows security architecture prevents "interactive" events from being sent to applications while a machine is logged or logged off. Because of this, it is important to set the task automatically log in if the task contains actions such as Send Keystrokes or Click Mouse . However, running applications, FTP, and other background processes are allowed to be performed in the background. When in an unattended back-office environment, for security reasons, it is preferable for a task to run completely in the background without needing to perform a log on; however this is only possible if the task does not simulate user interaction. If unsure it is advisable to test the task both ways before going live in a production environment.
When workstation is logged on:
If the task is triggered while a user is logged onto the workstation, AutoMate
can run the task in one of two ways:
Logged on user
AutoMate runs the task as the currently logged on user. For
example, if the user currently logged onto the workstation is joe@unisyn.com,
the task will use JoeÆs registry and application settings. This
default option is adequate for most situations.
Specified user
AutoMate runs the task as the specified user as set in the ôSpecified Userö
area (accessible via the Specified User button near the bottom of the
page). When
this option is selected, tasks will run in the context of the specified
user and act as if the task had been started by that user. For
example, if joe@unisyn.com is currently logged on, you can use this option
to run the task as sally@unisyn.com. When
the task runs, the registry and applications used by the task will act
as if Sally had started them, even though the task is running on JoeÆs
display. This
option should only be used when you need to run a task that uses applications
or performs background tasks that require elevated security privileges
or settings different from the logged on user.
When workstation is logged
off:
If the workstation is logged off and waiting for a user to log in when
the task triggers, AutoMate can attempt to do one of three things:
DonÆt Run
The task does not run when the workstation is logged off. Since
most tasks require interaction with the desktop, and such interaction
can only be done when a workstation is logged on, this default option
provides greatest compatibility with various scenarios.
Run in background
AutoMate will attempt to run the task behind the logon screen after silently
logging on the ôSpecified Userö. AutoMate
does not display a desktop, and therefore tasks that interact with application
interfaces will not function correctly. This
option is, however, recommended for non-interactive tasks that require
elevated rights, such as copying files from secure areas or automating
secure FTP transactions, without user knowledge or intervention.
Logon specified user
AutoMate will attempt to logon the user specified in the ôSpecified Userö
area. This
is done by emulating a user logon attempt at the keyboard (see the How AutoMate Logs On A User
topic for more information on how AutoMate does this). If
AutoMate determines that the logon attempt is successful, the task runs
as specified by the "When workstation is logged on" options
above.
When a workstation is locked:
If the workstation has been locked, either by a user, the Lock Workstation
action in AutoMate, or a screen saver, AutoMate can attempt one of three
things:
DonÆt Run
AutoMate does not run the task if the workstation is locked
Run while locked using interactive user
The task will run behind the locked workstation screen using the currently
logged on userÆs account. This
will cause tasks that require interaction with the desktop to operate
incorrectly or to fail, but does provides an excellent and secure way
to run tasks that do not require user interaction, such as unattended
file copies or FTP transfers.
Unlock Specified User
AutoMate will attempt to unlock the workstation using the ôSpecified Userö
account (see the How AutoMate Unlocks a Workstation topic for more information
on how AutoMate does this). Note
that the specified user must be the same user that is logged onto the
workstation when the task attempts to run. AutoMate
cannot forcibly log off a user if an attempt is made to unlock the workstation
with a user other than the current logged on account.
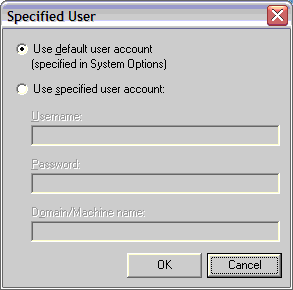
When you choose to logon or unlock the workstation using a specified user, you must define exactly what user AutoMate is to use. To do this, click the "Specified User" button. In the dialog that appears, choose:
Use default user account
This will use the user account
specified in the System Options under the Run
As tab. The
default Run As user should be set to the user that uses AutoMate most
frequently.
Use specified user account
When selected, allows the user to enter in a user specific for this task.
This account
will always override the default account.
See Also:
How AutoMate Unlocks a Workstation